Purpose
A Data Model describes the entities, classes, or data objects relevant to a domain, the attribute that are used to describe them, and the relationship among them to provide a common set of semantics for analysis and implementation.
Business Analysis Body of Knowledge® (BABOK®)
Data modelling is a set of tools and techniques used to understand and analyze how an organization should collect, update, and store data. It is a critical skill for business analysts who is involved with discovering, analyzing, and specifying changes for software systems to create and maintain information. The business analysts often need to analyze data as a part of making data modelling decisions, and this means that the data modelling can include some amount of data analysis technique. Data modelling is all about determining what data want to capture for specific purpose and then logically organize that data. The process of data modelling involves professional data modelers working closely with the business stakeholders, as well as potential users of the information system. Data modelling standards is used in all the projects requiring a standard means of defining and analyzing the data within an organization.
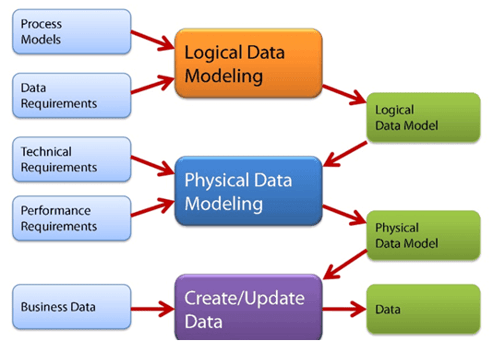
A data model usually takes the form of a diagram that is supported by the textual descriptions. It visually represents the elements that are important to the business, the attributes associated with those elements, and the relationship among them. They are frequently use din elicitation and requirements analysis, and it will also support the implementation and continuous improvement. There are three variations of data model in business analysis,
- Conceptual Data Model - It is independent of any solution or technology and can be used to represent how the business perceives its information. It can be used to establish a consistent vocabulary describing the business information.
- Physical Data Model - It is used by implementation subject matter experts to describe how a database is physically organized. It addresses concerns like concurrency, performance, and security.
- Logical Data Model - It is an abstraction of conceptual data model that incorporates rules of normalization to formally manage the integrity of the data and relationship.
Some of the articles related to Data modelling techniques are as follows,
- Data Modelling - https://www.guru99.com/data-modelling-conceptual-logical.html
- Guide to Data Modelling - http://faculty.washington.edu/burrows/IS300/dataModelingGuide.pdf
- Data Modelling Concepts - https://intellipaat.com/blog/data-modeling-tutorial-for-beginners/
- Data Modelling Design - https://darkopetrovic.com/pdf/Data-Modeling-and-Relational-Database-Design.pdf
- Data Modelling Techique - https://www.researchgate.net/publication/331197296_DATA_MODELING_TECHNIQUES_FOR_DATA_WAREHOUSE
- Introduction to Data Modelling - https://docs.mongodb.com/manual/core/data-modeling-introduction/
- Survey on Data Modelling - https://file.scirp.org/pdf/JSEA_2015123014504942.pdf
- Data Modelling Warehouse - https://www.teradatapoint.com/data-warehousing-data-modelling
- Data Modelling Approaches - https://www.snowflake.com/blog/support-multiple-data-modeling-approaches-with-snowflake/
- Data Modelling in Business Intelligence - https://www.redbooks.ibm.com/redbooks/pdfs/sg247138.pdf
The data model template represent the basic structure of the database, how data is stored, categorized, and managed within it. The template is the foundation of the database design and development effort. Some of the elements that is consider ion data modelling technique are,
- Entity - In data model, the organization keep the data on the entity. It represent something physical, organizational, abstract, or event. IT contains attributes and has the relationship to other entities in the model.
- Attribute - It defines the particular piece of information associated within an entity, including how much information can be captured in it, its allowable values, and the type of information it represents. It includes values such as,
- Name
- Meaning
- Description
- Relationship - The relationship between the entities provide the structure for the data model, specifically indicating which entities relate to which others and how. Specifications for a relationship typically indicate the number of minimum and maximum occurrences allowed on each side of that relationship.
- Diagrams - Both the data model and the class model may have one or more diagrams that show entities, attributes, and relationships. The diagram in data model is called as the entity-relationship diagram.
- Meta data - It optionally contain the meta data describing what the entities represent, when and why they were created or changed, how they should be used, how often they are used, when, and by whom.
Some of the books for Data modelling techniques are,
- Data Modelling: Practical Guide for Business | Steve Hoberman | https://www.amazon.com/Data-Modeling-Made-Simple-Professionals/dp/0977140067/ref=sr_1_8?dchild=1&keywords=data+modelling+books&qid=1593075092&sr=8-8
- Data Modelling: Beginner’s Guide | Andy Oppel | https://www.amazon.com/Data-Modeling-Beginners-Andy-Oppel/dp/0071623981/ref=sr_1_10?dchild=1&keywords=data+modelling+books&qid=1593075194&sr=8-10









